Leave Your Message
-
Phone
-
E-mail
-
Whatsapp
Ultraviolet (UV) drying light serves as a revolutionary tool in various industries. This technology harnesses UV radiation to cure inks, coatings, and adhesives efficiently. By using specific wavelengths, UV drying light accelerates the drying process significantly.
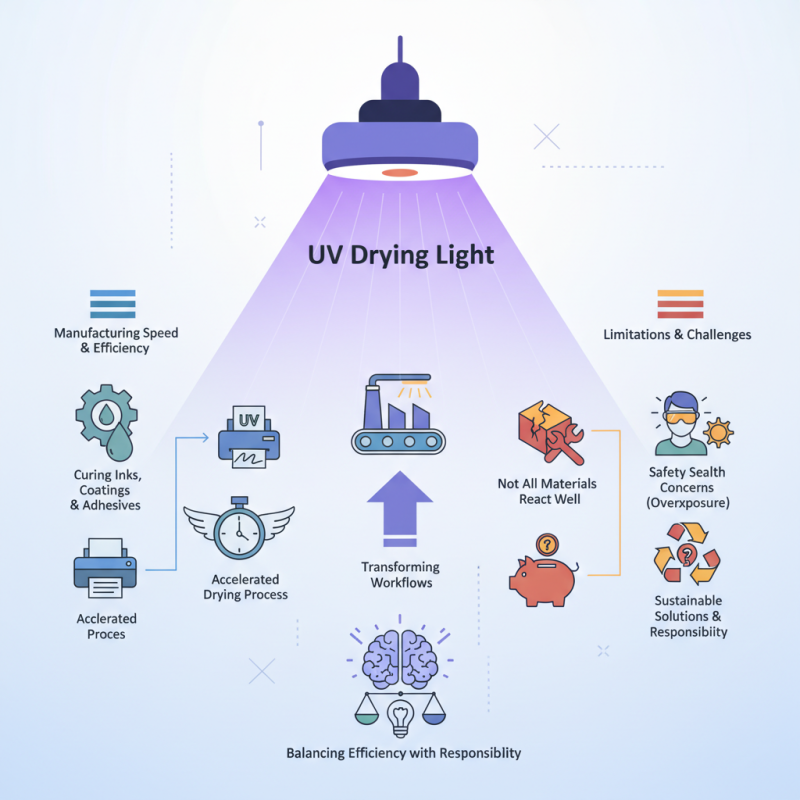
In manufacturing, speed and efficiency are crucial. The UV drying light provides benefits that can transform workflows. However, it is essential to understand its limitations as well. For instance, not all materials react well to this process.
Some manufacturers may face challenges. The initial setup can be costly and complex. Regular maintenance is also necessary for optimal performance. The potential for overexposure to UV light raises concerns in safety and health practices. Moreover, exploring more sustainable solutions remains a vital conversation. Balancing efficiency with environmental responsibility is an ongoing challenge.

UV drying light is a revolutionary technology used in various industries. This method employs ultraviolet light to cure or dry inks, coatings, and adhesives. A report by the American Coatings Association indicates that UV curing has gained significant traction, particularly in the printing and woodworking sectors.
The process of UV drying works by using UV light to initiate a photochemical reaction. This reaction transforms liquid materials into solid forms rapidly. Industries benefit from this technology due to its speed. For example, UV light can dry a coat in seconds, compared to conventional methods that may take hours. Additionally, it is more environmentally friendly. UV curing generates fewer volatile organic compounds (VOCs), which contributes to safer working conditions.
However, there are challenges. Not all materials are suitable for UV curing. For instance, some substrates may yellow or deform under UV light. This limits its application in certain scenarios. Companies must invest time in researching compatible materials to avoid such issues. Inadequate understanding can lead to costly mistakes in production. Thus, while UV drying light offers significant advantages, careful consideration is essential for its effective implementation.
UV drying technology utilizes ultraviolet light to accelerate drying processes in various applications. This method is widely used in printing, coatings, and adhesives. The UV light cures or hardens materials by triggering a chemical reaction. As the light hits the surface, it activates photoinitiators in the coating or ink. This reaction produces strong bonds, resulting in a dry and durable finish.
The principles behind UV light technology are fascinating. The energy emitted initiates a process that transforms liquid components into solid forms. This is efficient and often faster than conventional drying methods. The emitted UV light penetrates the materials, ensuring uniform curing throughout. It's essential to consider the type of UV light used, as different wavelengths can yield different results.
**Tip:** Always test your materials with smaller samples before scaling up. Ensure compatibility and optimal results.
However, the technology isn't perfect. Some materials might not cure adequately under UV light. Thicker layers may lead to under-curing, risking the end product’s integrity. It's crucial to adjust settings based on material type and desired thickness for best results.
**Tip:** Keep an eye on the curing process. Adjust exposure time based on your materials to avoid imperfections.
UV drying light systems consist of key components that work together to accelerate the drying process of inks, coatings, and adhesives. At the core, UV lamps emit ultraviolet light, triggering a chemical reaction in the material. This reaction cures or hardens the substances quickly, making it an efficient option for various industries.
The system usually includes a power source, which supplies energy to the lamps. Reflectors are also crucial; they direct the light onto the surface being treated. Additionally, a conveyer belt often transports items under the lamp. Each part plays a vital role in ensuring that the UV light reaches every inch of the surface, optimizing the drying performance.
Tips: It's essential to select the right wavelength for your specific application. Not all materials respond the same way to UV light. Test your process on a small scale before full implementation. Also, maintain your equipment regularly. A dirty lamp will emit less effective light. Watch for discoloration in finished products; it might indicate uneven curing. Remember, every application can have unique challenges. Adjust your setup accordingly.

UV drying lights have become essential in various industries due to their efficiency. They utilize ultraviolet light to cure or dry materials quickly, reducing wasted time. This technology is especially prevalent in printing, coatings, and adhesives. In these sectors, the ability to dry surfaces almost instantly enhances productivity.
One significant advantage of UV drying light is its ability to create strong bonds. Products can be handled sooner after drying, minimizing delays in production lines. Additionally, this method is environmentally friendly. Traditional drying methods often require solvents, which can be harmful. UV lights typically emit fewer volatile organic compounds, making processes cleaner.
However, there are challenges. Not all materials respond well to UV curing. Some require specific wavelengths or exposure times. Additionally, operators must be trained properly. Incorrect setup can lead to ineffective curing. These factors need careful consideration. Users must find the right balance to maximize efficiency and quality in their processes.
When using UV drying lights, safety should be a primary concern. The UV rays emitted can pose risks to skin and eyes. Direct exposure can lead to burns or even long-term damage. Research indicates that UV radiation can increase the risk of skin cancer. According to the American Academy of Dermatology, exposure to UV light should be limited. Protective eyewear and skin coverage are essential when operating these lights.
Best practices are vital in utilizing UV drying technology effectively. Ensure that the workspace has adequate ventilation. Proper distance from the light source can mitigate risks. Aim for a distance of around 12 inches to minimize exposure while achieving effective drying. Regular calibration of UV equipment enhances efficiency. This practice not only improves performance but also avoids overexposing surfaces and risking damage. Monitoring the intensity of UV rays ensures effective drying without compromising safety.
Training staff is crucial. Comprehensive education on UV light hazards can prevent accidents. An industry report from the UV Technology Association states that companies with safety training see a 30% reduction in workplace incidents. Regular workshops and safety drills can reinforce these practices. Remember, while UV drying can optimize efficiency, it demands respect and responsibility in its use.
| Aspect | Details |
|---|---|
| Definition | UV drying light refers to ultraviolet light used to accelerate the curing process of certain materials. |
| Mechanism | UV light initiates a photochemical reaction that hardens materials like inks, coatings, and adhesives. |
| Applications | Used in printing, automotive, woodworking, and electronics for quick drying and curing. |
| Safety Considerations | Proper protective gear, such as goggles and gloves, should be worn to prevent skin and eye exposure. |
| Best Practices | Ensure proper ventilation, follow manufacturer guidelines, and regularly maintain equipment for efficiency. |